|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||

PhiYFP
SUPPORTRESOURCES |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PhiYFP and PhiYFP-m are the mutants of a natural yellow fluorescent protein from Phi-Yellow proteins have excitation/emission maxima at 525 and 537 nm, respectively. They exhibit lower brightness and maturation rate than TurboYFP, but are more suitable for generation of stably transfected cell lines. The emission wavelength of these proteins is ideally positioned between those of green and red fluorescent proteins, allowing easy separation of these fluorescent tags by flow cytometry using common channels of detection and a single laser excitation line. |
Main properties
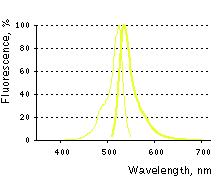
PhiYFP normalized excitation (thin line) and emission (thick line) spectra. |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Recommended filter sets and antibodies
The proteins can be recognized using Anti-TurboYFP (Cat.# AB605) antibodies available from Evrogen.
Phi-Yellow proteins can be detected using Omega Optical filter set XF104-3 or Chroma Technology Corp. filter set 42003 ("ZsYellow1").
Performance and use
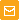
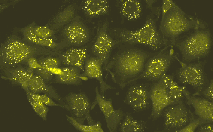
Phi-Yellow proteins can be easily expressed and detected in a wide range of organisms. Mammalian cells transiently transfected with PhiYFP and PhiYFP-m expression vectors produce bright fluorescence in 10-12 hours after transfection. No cytotoxic effects or visible protein aggregation are observed.
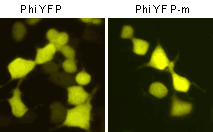 | Fluorescent microscopy of transiently transfected mammalian cells expressing Phi-Yellow proteins.
|
Suitability of Phi-Yellow proteins to generate stably transfected cells has been proven by Marinpharm company.
Despite dimerization capacity, Phi-Yellow proteins demonstrate successful performance in fusions with subcellular localization signals and many cellular proteins. However, we recommend that you use TagFPs for protein labeling applications.
Important note: PhiYFP allows generation of fusions to its N-terminus, whereas PhiYFP-m is optimized to generate fusions to its C-terminus. PhiYFP can not be used to generate C-terminal fusions.
Phi-Yellow proteins can be used in multicolor labeling applications with blue, cyan, green, red, and far-red fluorescent dyes.
| Variant | Description | Related vector | Cat.# | Click for image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| PhiYFP | PhiYFP codon usage is optimized for high expression in mammalian cells [Haas et al., 1996], but it can be successfully expressed in many other heterological systems. PhiYFP allows generation of fusions to its N-terminus but unsuited to generate C-terminal fusions. |
|
FP602 |
|
|
|
FP604 | |||
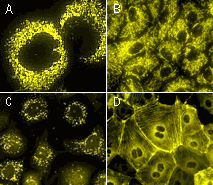
| PhiYFP-mito fusion | A mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) is fused to the PhiYFP N-terminus. MTS was derived from the subunit VIII of human cytochrome C oxidase [Rizzuto et al., 1989; Rizzuto et al., 1995]. When expressed in mammalian cells, this variant provides green fluorescent labeling of mitochondria. |
|
FP607 |
|
| PhiYFP-m-peroxi fusion | Peroxisomal targeting signal [Gould et al., 1989] encoding tripeptide SKL was fused to the 3' end of PhiYFP-m sequence. This tripeptide targets the fusion protein to the matrix of peroxisomes. |
|
FP606 |
|
References:
- Gould SJ, Keller GA, Hosken N, Wilkinson J, Subramani S. A conserved tripeptide sorts proteins to peroxisomes. J Cell Biol. 1989; 108 (5):1657-64. / pmid: 2654139
- Haas J, Park EC, Seed B. Codon usage limitation in the expression of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. Curr Biol. 1996; 6 (3):315-24. / pmid: 8805248
- Rizzuto R, Brini M, Pizzo P, Murgia M, Pozzan T. Chimeric green fluorescent protein as a tool for visualizing subcellular organelles in living cells. Curr Biol. 1995; 5 (6):635-42. / pmid: 7552174
- Rizzuto R, Nakase H, Darras B, Francke U, Fabrizi GM, Mengel T, Walsh F, Kadenbach B, DiMauro S, Schon EA. A gene specifying subunit VIII of human cytochrome c oxidase is localized to chromosome 11 and is expressed in both muscle and non-muscle tissues. J Biol Chem. 1989; 264 (18):10595-600. / pmid: 2543673
- Shagin DA, Barsova EV, Yanushevich YG, Fradkov AF, Lukyanov KA, Labas YA, Semenova TN, Ugalde JA, Meyers A, Nunez JM, Widder EA, Lukyanov SA, Matz MV. GFP-like proteins as ubiquitous metazoan superfamily: evolution of functional features and structural complexity. Mol Biol Evol. 2004; 21 (5):841-50. / pmid: 14963095
|
Copyright 2002-2023 Evrogen. All rights reserved. Evrogen JSC, 16/10 Miklukho-Maklaya str., Moscow, Russia, Tel +7(495)988-4084, Fax +7(495)988-4085, e-mail:evrogen@evrogen.com |