|
Caspase-3 apoptosis sensor Casper3-BG
- Early detection of Caspase-3 activity onset
- High sensitivity
- Direct expression in cells
- No exogenous chemical compounds required
- Recommended for early detection of apoptosis
Performance and use
The excellent performance of Casper3-BG sensor has been demonstrated in vivo on the example of HeLa cells staurosporine-induced apoptosis [Subach et al., 2008]. The two-filter method of sensitized FRET measurements [Gordon et al., 1998] on a pixel-by-pixel basis was applied, as described in [Galperin et al., 2004]. The initial mean FRET efficiency in vivo normalized to donor fluorescence was 51.5%. Following 40-80 min exposure to 1 mM staurosporine, the FRET gradually dropped to zero before the shrinking of cells characteristic to apoptosis. The large FRET efficiency of the TagBFP-TagGFP2 pair enabled the detection of even weak proteolitic activity in each cell at the beginning of apoptosis, when only a fraction of the substrate was cleaved.
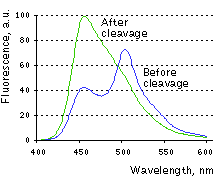 | Change in Casper3-BG emission spectra upon the cleavage of DEVD sequence in vitro.
|
|---|
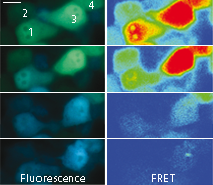 | 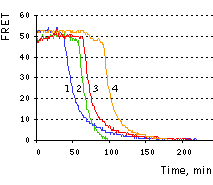 | Imaging of FRET intensity in staurosporine-treated HeLa cells.
Cells treated with staurosporine are shown as overlaid fluorescent images of blue and green channels (left panels). The corrected FRET signals are shown in pseudocolor (right panels). Scale bar represents 10 μm.
On the right, time course of corrected FRET signal for the four cells is shown.
|
|---|
References:
-
Galperin E, Verkhusha VV, Sorkin A.
Three-chromophore FRET microscopy to analyze multiprotein interactions in living cells.
Nat Methods. 2004; 1 (3):209-17. / pmid: 15782196
-
Gordon GW, Berry G, Liang XH, Levine B, Herman B.
Quantitative fluorescence resonance energy transfer measurements using fluorescence microscopy.
Biophys J. 1998; 74 (5):2702-13. / pmid: 9591694
-
Subach OM, Gundorov IS, Yoshimura M, Subach FV, Zhang J, Gruenwald D, Souslova EA, Chudakov DM, Verkhusha VV.
Conversion of Red Fluorescent Protein into a Bright Blue Probe.
Chem Biol. 2008; 15 (10):1116-24. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.08.006 / pmid: 18940671
|