|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The vector sequence has been compiled using the information from sequence databases, published literature, and other sources, together with partial sequences obtained by Evrogen. This vector has not been completely sequenced. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Download
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nhe I | Bgl II | Sac I | Hind III | EcoR I | Sal I | Kpn I | Apa I | BamH I | Age I | TurboFP602 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Afe I | Xho I | Pst I | Sac II | Nco I* | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GCT | A.GC | G.CT | A.CCG.GAC.TC | A.GAT. | CT | C. | GAG. | CTC. | AAG.CTT. | C | GA.ATT. | C | TG.CA | G. | TCG.AC | G.GTA. | CC | G.C | GG. | G | CC.C | G | G.G | AT.CC | A.CCG.GT | C.GCC.A | CC. | ATG.G | TG.GGT |
* – not unique site.
Vector description
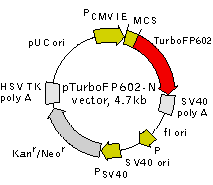
pTurboFP602-N is a mammalian expression vector encoding true-red fluorescent protein TurboFP602 (see reporter description). The vector allows generation of fusions to the TurboFP602 N-terminus and expression of TurboFP602 fusions or TurboFP602 alone in eukaryotic (mammalian) cells.
TurboFP602 codon usage is optimized for high expression in mammalian cells (humanized) [Haas et al., 1996]. To increase mRNA translation efficiency, Kozak consensus translation initiation site is generated upstream of the TurboFP602 coding sequence [Kozak, 1987]. Multiple cloning site (MCS) is located between PCMV IE and TurboFP602 coding sequence.
The vector backbone contains immediate early promoter of cytomegalovirus (PCMV IE) for protein expression, SV40 origin for replication in mammalian cells expressing SV40 T-antigen, pUC origin of replication for propagation in
SV40 early promoter (PSV40) provides neomycin resistance gene (Neor) expression to select stably transfected eukaryotic cells using G418. Bacterial promoter (P) provides kanamycin resistance gene expression (Kanr) in
Generation of TurboFP602 fusion proteins
A localization signal or a gene of interest can be cloned into MCS of the vector. It will be expressed as a fusion to the TurboFP602 N-terminus when inserted in the same reading frame as TurboFP602 and no in-frame stop codons are present. The inserted sequence should contain an initiating ATG codon. TurboFP602-tagged fusions retain fluorescent properties of the native protein allowing fusion localization in vivo. Unmodified vector will express TurboFP602 when transfected into eukaryotic (mammalian) cells.
Note: The plasmid DNA was isolated from dam+-methylated
Expression in mammalian cells
pTurboFP602-N vector can be transfected into mammalian cells by any known transfection method. CMV promoter provides strong, constitutive expression of TurboFP602 or its fusions in eukaryotic cells. If required, stable transformants can be selected using G418 [Gorman, 1985].
Propagation in
Suitable host strains for propagation in
Location of features
PCMV IE: 1-589
Enhancer region: 59-465
TATA box: 554-560
Transcription start point: 583
MCS: 592-678
TurboFP602
Kozak consensus translation initiation site: 672-682
Start codon (ATG): 679-681
Stop codon: 1384-1386
SV40 early mRNA polyadenylation signal
Polyadenylation signals: 1540-1545 & 1569-1574
mRNA 3' ends: 1578 & 1590
f1 single-strand DNA origin: 1637-2092
Bacterial promoter for expression of Kanr gene
-35 region: 2154-2159
-10 region: 2177-2182
Transcription start point: 2189
SV40 origin of replication: 2433-2568
SV40 early promoter
Enhancer (72-bp tandem repeats): 2266-2337 & 2338-2409
21-bp repeats: 2413-2433, 2434-2454 & 2456-2476
Early promoter element: 2489-2495
Major transcription start points: 2485, 2523, 2529 & 2534
Kanamycin/neomycin resistance gene
Neomycin phosphotransferase coding sequences:
Start codon (ATG): 2617-2619
Stop codon: 3409-3411
G->A mutation to remove Pst I site: 2799
C->A (Arg to Ser) mutation to remove BssH II site: 3145
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) thymidine kinase (TK) polyadenylation signal
Polyadenylation signals: 3647-3652 & 3660-3665
pUC plasmid replication origin: 3996-4639
References:
- Gorman C. High efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells. In DNA cloning: A Practical Approach, Vol. II. Ed. D. M. Glover. (IRL Press, Oxford, U.K.). 1985; 143-90.
- Haas J, Park EC, Seed B. Codon usage limitation in the expression of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. Curr Biol. 1996; 6 (3):315-24. / pmid: 8805248
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987; 15 (20):8125-48. / pmid: 3313277
Notice to Purchaser:
TurboFP602-related materials (also referred to as "Products") are intended for research use only. The Products are covered by U.S. Pat. 8,138,320; European Pat. 1994149; and other Evrogen Patents and/or Patent applications pending. By use of these Products, you accept the terms and conditions of the applicable Limited Use Label License.
|
Copyright 2002-2023 Evrogen. All rights reserved. Evrogen JSC, 16/10 Miklukho-Maklaya str., Moscow, Russia, Tel +7(495)988-4084, Fax +7(495)988-4085, e-mail:evrogen@evrogen.com |