|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The vector sequence has been compiled using the information from sequence databases, published literature, and other sources, together with partial sequences obtained by Evrogen. This vector has not been completely sequenced. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Download
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vector description
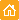
pKillerOrange-dMito is a mammalian expression vector encoding mitochondria-targeted KillerOrange (see reporter description). KillerOrange codon usage is optimized for high expression in mammalian cells (humanized) [Haas et al., 1996]. Duplicated mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) is fused to the KillerOrange N-terminus. MTS was derived from the subunit VIII of human cytochrome C oxidase [Rizzuto et al., 1989; Rizzuto et al., 1995].
pKillerOrange-dMito vector can be used as a source of dMTS-KillerOrange hybrid sequence. The vector backbone contains unique restriction sites that permit its excision and further insertion into expression vector of choice. Alternatively, dMTS-KillerOrange coding sequence can be amplified by PCR.
Note: The plasmid DNA was isolated from dam+-methylated
The vector backbone contains immediate early promoter of cytomegalovirus (PCMV IE) for protein expression, SV40 origin for replication in mammalian cells expressing SV40 T-antigen, pUC origin of replication for propagation in
SV40 early promoter (PSV40) provides neomycin resistance gene (Neor) expression to select stably transfected eukaryotic cells using G418. Bacterial promoter (P) provides kanamycin resistance gene expression (Kanr) in
Expression in mammalian cells
pKillerOrange-dMito vector can be transfected into mammalian cells by any known transfection method. CMV promoter provides strong, constitutive expression of mitochondria-targeted KillerOrange in eukaryotic cells. If required, stable transformants can be selected using G418 [Gorman, 1985].
Propagation in
Suitable host strains for propagation in
Location of features
PCMV IE: 1-589
Enhancer region: 59-465
TATA box: 554-560
Transcription start point: 583
KillerOrange-dMito fusion
Start codon (ATG): 597-599
Mitochondrial localization signal 1 (MLS-1): 597-689
Mitochondrial localization signal 2 (MLS-2): 690-782
Start of KillerOrange coding sequence(GAG): 801-803
Stop codon: 1509-1511
SV40 early mRNA polyadenylation signal
Polyadenylation signals: 1664-1669 & 1693-1698
mRNA 3' ends: 1702 & 1714
f1 single-strand DNA origin: 1761-2216
Bacterial promoter for expression of Kanr gene
-35 region: 2278-2283
-10 region: 2301-2306
Transcription start point: 2313
SV40 origin of replication: 2557-2692
SV40 early promoter
Enhancer (72-bp tandem repeats): 2390-2461 & 2462-2533
21-bp repeats: 2537-2557, 2558-2578 & 2580-2600
Early promoter element: 2613-2619
Major transcription start points: 2609, 2647, 2653 & 2658
Kanamycin/neomycin resistance gene
Neomycin phosphotransferase coding sequences:
Start codon (ATG): 2741-2743
Stop codon: 3533-3535
G->A mutation to remove Pst I site: 2923
C->A (Arg to Ser) mutation to remove BssH II site: 3269
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) thymidine kinase (TK) polyadenylation signal
Polyadenylation signals: 3771-3776 & 3784-3789
pUC plasmid replication origin: 4120-4763
References:
- Gorman C. High efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells. In DNA cloning: A Practical Approach, Vol. II. Ed. D. M. Glover. (IRL Press, Oxford, U.K.). 1985; 143-90.
- Haas J, Park EC, Seed B. Codon usage limitation in the expression of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. Curr Biol. 1996; 6 (3):315-24. / pmid: 8805248
- Rizzuto R, Brini M, Pizzo P, Murgia M, Pozzan T. Chimeric green fluorescent protein as a tool for visualizing subcellular organelles in living cells. Curr Biol. 1995; 5 (6):635-42. / pmid: 7552174
- Rizzuto R, Nakase H, Darras B, Francke U, Fabrizi GM, Mengel T, Walsh F, Kadenbach B, DiMauro S, Schon EA. A gene specifying subunit VIII of human cytochrome c oxidase is localized to chromosome 11 and is expressed in both muscle and non-muscle tissues. J Biol Chem. 1989; 264 (18):10595-600. / pmid: 2543673
Notice to Purchaser:
KillerOrange-related materials (also referred to as "Products") are intended for research use only.
|
Copyright 2002-2023 Evrogen. All rights reserved. Evrogen JSC, 16/10 Miklukho-Maklaya str., Moscow, Russia, Tel +7(495)988-4084, Fax +7(495)988-4085, e-mail:evrogen@evrogen.com |